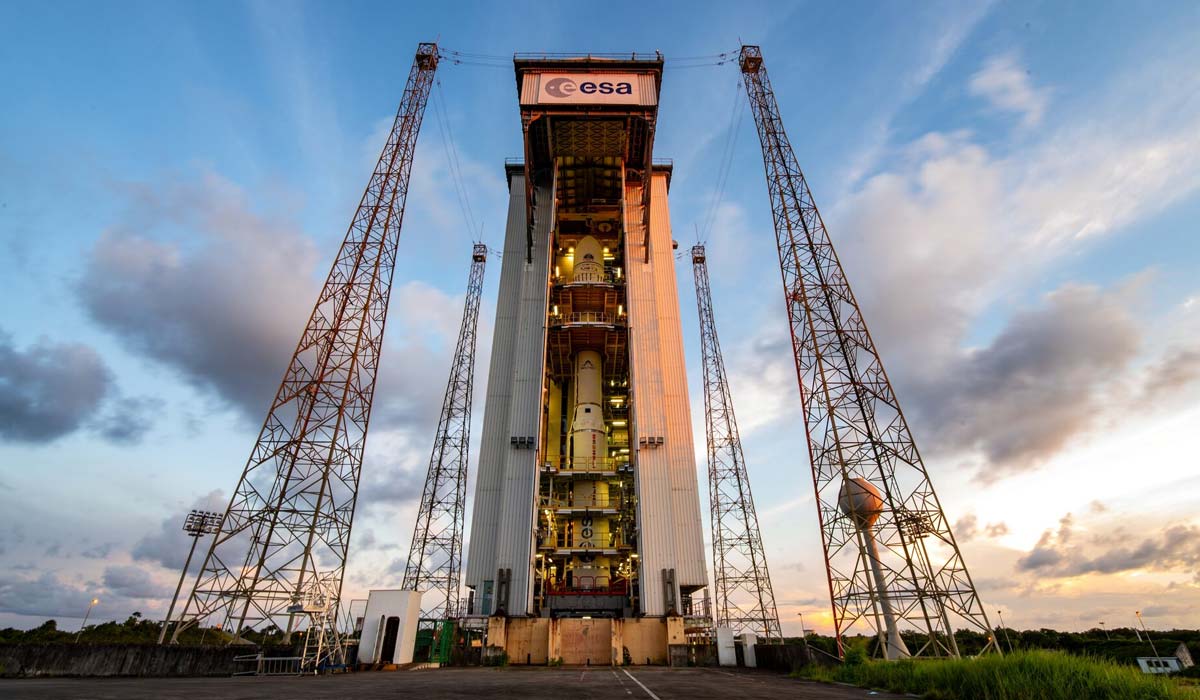
Europe’s Vega C rocket is set to take on another important mission, with plans confirmed to launch a Brazilian satellite into space. The upcoming flight highlights both the growing international role of Europe’s small-to-medium launch vehicle and Brazil’s continued investment in strengthening its space-based capabilities.
The mission comes as Vega C continues to return to a regular launch rhythm, supporting commercial, scientific, and governmental payloads for customers around the world.
Vega C’s Role in Europe’s Launch Portfolio
Vega C is operated by Arianespace and built under the leadership of Avio, with contributions from several European partners. It represents an upgraded version of the original Vega rocket, offering increased payload capacity, improved performance, and greater flexibility for placing satellites into a variety of orbits.
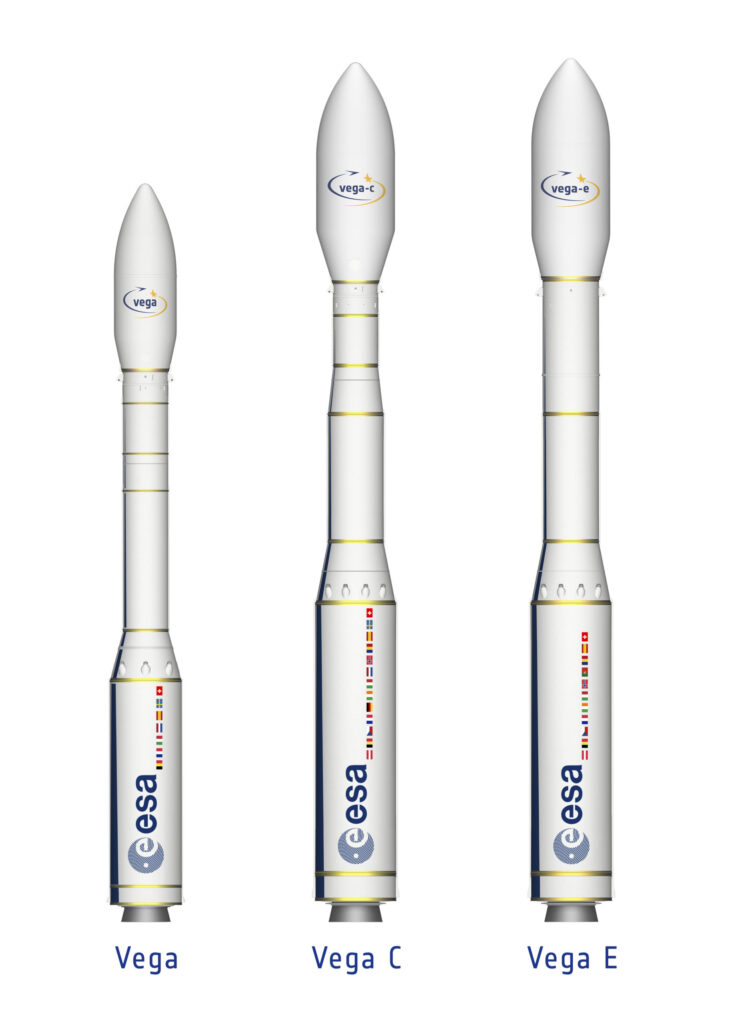

Designed primarily for small satellites and institutional missions, Vega C fills an important niche within Europe’s launch lineup. While Ariane 6 is intended for heavier payloads, Vega C provides access to space for lighter spacecraft, Earth observation missions, and constellation deployments.
The rocket stands about 35 meters tall and can deliver payloads of roughly 2,300 kilograms into low Earth orbit, making it suitable for satellites like the one Brazil is preparing to send into space.
The Brazilian Satellite Mission
The satellite scheduled for launch is part of Brazil’s broader efforts to expand its space infrastructure, particularly in the areas of communications, Earth monitoring, and environmental management.
Brazil has increasingly relied on satellite technology for applications such as:
- Tracking deforestation in the Amazon
- Monitoring agriculture and water resources
- Supporting disaster response and emergency planning
- Strengthening national communications networks
By placing a new satellite into orbit, Brazil aims to enhance its ability to gather data and provide services that are essential for both economic development and national security.
Although full technical details of the spacecraft have not yet been widely released, the mission reflects Brazil’s growing presence as a space actor in Latin America.
International Cooperation in Space
The Vega C launch also demonstrates the importance of international partnerships in today’s space sector. Launch services are increasingly global, with satellites often built in one country, financed in another, and launched from facilities operated by international providers.
For Brazil, selecting Vega C as the launch vehicle underscores Europe’s continued relevance in the competitive global launch market. For Arianespace, the mission strengthens ties with emerging space nations and reinforces Vega C’s position as a reliable option for institutional payloads.

Such collaborations are becoming more common as more countries develop space programs but do not necessarily maintain domestic launch capabilities.
Vega C’s Recent Progress and Return to Flight
Vega C has faced challenges since its introduction, including a mission failure that temporarily grounded the rocket while engineers investigated and implemented corrective measures.
Following that period, the program has focused on improving reliability and returning Vega C to a steady launch cadence. Each successful mission is considered an important step in rebuilding confidence among institutional and commercial customers.
The upcoming Brazilian satellite launch will therefore be closely watched, not only for its value to Brazil’s space ambitions, but also as part of Vega C’s broader operational recovery.
Launch Site and Timeline
The mission is expected to lift off from Europe’s Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, a key launch site located near the equator. This geographic advantage allows rockets to benefit from Earth’s rotational speed, improving efficiency and payload performance.
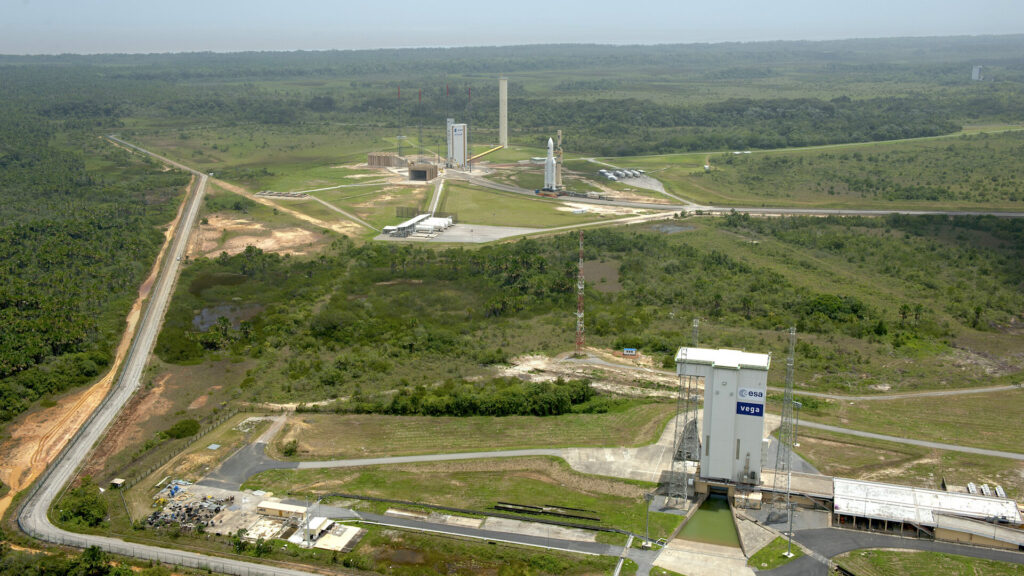

Kourou has long served as the primary base for European launch operations and is regularly used for Ariane, Soyuz (in the past), and Vega-family rockets.
Arianespace has indicated that Vega C’s manifest will remain active through the coming year, supporting a mix of European institutional missions and international customer payloads.
Why This Launch Matters
The launch carries significance on multiple levels:
- For Brazil, it supports national priorities in monitoring, communications, and technology development.
- For Vega C, it represents another opportunity to demonstrate reliability and strengthen its role in the global market.
- For international space cooperation, it highlights the interconnected nature of modern satellite missions.
As demand for satellite services continues to rise worldwide, access to dependable launch options remains critical.
Looking Ahead
Vega C is expected to play a central role in Europe’s ability to provide independent access to space, especially for smaller payloads. At the same time, countries like Brazil are expanding their use of orbital infrastructure to support environmental, economic, and security needs.
The upcoming mission, sending a Brazilian satellite into orbit aboard Vega C, reflects these parallel trends: a more global space industry, growing satellite dependence, and continued investment in launch systems capable of meeting diverse customer demands.
With preparations underway, the flight is poised to become another notable chapter for both the Vega C program and Brazil’s evolving space strategy.